Deep learning methods for segmentation of lines in pediatric chest radiographs
Abstract
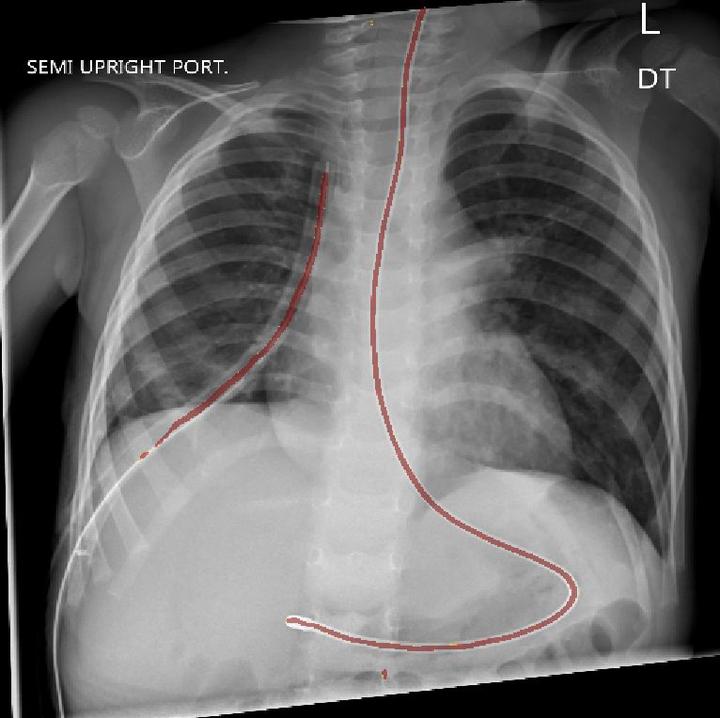
Surgical procedures often require the use of catheters, tubes, and lines, collectively called lines. Misplaced lines can cause serious complications, such as pneumothorax, cardiac perforation, or thrombosis. To prevent these problems, radiologists examine chest radiographs after insertion and throughout intensive care to evaluate their placement. This process is time consuming, and incorrect interpretations occur with notable frequency. Fast and reliable automatic interpretations could potentially reduce the cost of these surgical operations, decrease the workload of radiologists, and improve the quality of care for patients. We develop a segmentation model which can highlight the medically relevant lines in pediatric chest radiographs using deep learning. We propose a two-stage segmentation network which first classifies whether images have medically relevant lines and then segments images with lines. For the segmentation stage, we use the popular U-Net architecture substituting the encoder path with multiple state-of-the-art CNN encoders. Our study compares the performance of different permutations of model architectures for the task of highlighting lines in pediatric chest radiographs and demonstrates the effectiveness of the two-stage architecture.